Most makers of 35mm slide projectors offered a bread-and-butter plastic-barrel 85/2.8 and an optically superior upgrade that could be specified at purchase or retro-fitted. These lenses typically (though not always) jumped to 90mm but were always a little faster: commonly f2.4 or f2.5. The glass wasn’t just longer, it was deeper: deluxe options eschewed triplets in favour of better corrected four-, five- or six-element Tessar, Planar and Gauss designs – commonly air-spaced, often in as many groups as elements. The best came close to being fully apochromatic.
As taking lenses they tend to have more consistent performance across the frame and much better colour rendition. Combined with the extra speed and smoother bokeh, and given the relatively minor difference in price, these are well worth the extra: they are significantly better (though not necessarily more characterful) portrait lenses than their slower siblings.
Before drilling down into ‘character’, let’s consider the sharpness of each lens when plucked from a projector and used for image capture at short and long distances – compared to the best and worst standard projector lenses, and familiar benchmarks. Note that projected image quality is about more than the lens: the imaging path is influenced by alignment tolerances, the condenser lens, bulb specification and magnification. Therefore the following results don’t necessarily establish a pecking order for the best projectors. They relate solely to performance as taking lenses, paired with a 35mm sensor. The following table summarises the performance of all premium lenses at this focal length:
| Lens Name | Fitted to | Near zA | Near zB | Far zA | Far zC | Mark |
| Agfa Color-Agolon 90/2.5 | 7.65 | 6.4 | 7.6 | 6.5 | 70% | |
| Braun Super-Paxon S 90/2.5 | ||||||
| Braun Super-Paxon 90/2.5 | ||||||
| Braun Ultralit PL 90/2.4 | 8.4 | 7.5 | 8.4 | 7.9 | 81% | |
| Docter Doctarlux 90/2.5 | Kodak AV Series | 7.7 | 5.8 | 7.8 | 6.3 | 69% |
| Enna Ennalyt 90/2.5 | 7.9 | 6.8 | 8.3 | 6.9 | 75% | |
| Kindermann 90mm f2.4 MC | ||||||
| Kodak Retinar 90/2.5 | ||||||
| Kodak Ektapro Select 93/2.5 | Kodak Ektapro | 8.15 | 5.9 | 8.2 | 6.2 | 71% |
| Leitz Colorplan-P 90/2.5 [V1] | Pradovit Series | 7.6 | 7.3 | 7.7 | 6.6 | 73% |
| Leitz Colorplan-P 90/2.5 [V2] | Pradovit Series | 8.3 | 7.1 | 7.4 | 7.0 | 75% |
| Leica Super-Colorplan-P2 90/2.5 | 8.5 | 8.0 | 8.5 | 7.9 | 82% | |
| Liesegang Sankar 90mm f2.5 MC | ||||||
| Reflecta Agomar MC 90/2.4 | Diamator Series | 8.2 | 7.7 | 7.8 | 7.1 | 77% |
| Revuetar 90mm f2.5 | ||||||
| Rollei (Isco) V/S-Heidosmat 90/2.4 | ||||||
| Rollei (Isco) V/S-Projar 90/2.5 | ||||||
| Rollei S-Projar 90/2.5 | 8.4 | 6.7 | 7.6 | 6.7 | 74% | |
| Rollei AV-Apogon 90/2.4 | 300P/330P/535P | 9.05 | 7.6 | 8.9 | 7.6 | 83% |
| Rollei AV-Apogon 90/2.8 | Rollei 66P | |||||
| Schneider Xenotar 90/2.4 | 7.8 | 6.5 | 8.3 | 6.9 | 74% | |
| Zeiss Super Talon 90/2.5 | Ikon Series | 8.1 | 6.5 | 8.2 | 6.4 | 73% |
| Zeiss P-Planar 90/2.5 | Ikon Series | |||||
| Zeiss P-Sonnar 90/2.5 | Ikon Series | 7.9 | 6.7 | 8.0 | 6.5 | 73% |
| For comparison . . . | ||||||
| Agfa Agomar 85mm [V2] | 8.0 | 6.9 | 8.3 | 6.4 | 74% | |
| Agfa Color-Agolar 60/2.8 | ||||||
| Rollei Heidosmat 85/2.8 | 6.1 | 5.6 | 6.3 | 5.4 | 59% | |
| Schneider Vario-Xenotar 70-120/3.5 | 8.1 | 7.8 | 8.3 | 7.6 | 80% | |
| Docter Doctarlux 150/2.8 | 8.3 | 7.4 | 8.7 | 7.7 | 80% | |
| Schneider Apo-Componon 60mm at f4 | 9.15 | 8.6 | 8.7 | 8.2 | 87% | |
| Sigma 50mm Art at f2.8 | 9.2 | 8.7 | 9.4 | 9.2 | 91% |
In summary:
- Slide projector lenses follow the pattern of cine projector lenses when deployed as taking lenses: often very sharp in Zone 1; never sharp in Zone 3. Even then, we only reach ‘good enough’ levels compared to the brilliant resolution of modern optics.
- The Rollei AV-Apogon 90/2.4 has the best centre-frame performance of any slide projector lens tested so far. The Leica SuperColorplan-P2 90/2.4 has the best Zone C (35mm corner) performance.
- Distance matters. Some projector lenses are sharper close up; some at typical projection distances or longer. Even the Schneider Apo-Componon 60, which comes close to fully resolving a full frame sensor, delivers relatively low resolution at long distance.
- Most 85/2.8 projector lenses perform like the Rollei Heidosmat: the Agfa Agomar 85mm is a rare exception that matches the higher standard of these faster 90mm options.
- Few zoom projector lenses perform like the Vario-Xenotar 70-120/3.5 – but these figures are recorded at its peak 70mm setting where there is also geometric distortion and vignetting in Zone C. From 90-120mm, this lens dips to 70-75%. It’s also much easier to record good resolution at f3.5 than f2.4.
Notes Re: Specific Lenses
Braun Super-Paxon and Ultralit
Whereas the Zeiss Super-Talons are quite distinct from the standard Talon, not all Super-Paxons (sometime the hyphen is omitted) are super, and not every Ultralit was ultra. All the f2.8 Super-Paxons are triplets, as is the Ultralit PL 85. It’s a universal truth among 35mm projector lenses that the f2.4 or f2.5 offers superior performance, or at least guarantees the optic consists of four or more elements.
Kodak Ektapro Select 93/2.5
This lens is also known as the AV-Retinar, and AV-2000. Although it’s a high-end, collectable, five element optic with an image circle comfortably large enough for 6×6 and more, it’s not well suited to a 35mm sensor: the focal-flange distance is so short (15mm – even assuming a flange in plane with the rear element) that focusing is very difficult. Image quality is a casualty of this uncomfortable geometry. Chasseur d’Images awarded this lens 3/5 in its survey of project lens performance in XX.
Kodak Retinar 90mm f2.5
We presently believe the 90mm f2.5 lenses branded Kodak Retinar, Rollei S-Heidosmat, Rollei-S-Projar and Rollei V/S-Projar to be the same five-element lens in continuous prodution by Isco from c.1975-1990, modified over time with improved coatings.
Leica Colorplan V1 and V2 (pre-P versions)
Version 1 Leitz-branded Colorplan lenses came in silver metal barrels and were fitted to Pradovit projectors sold XX-XX. The five-element design was manufactured exclusively in Germany. Version 2 was upgraded to a six-element design with production split during XX-XX between Germany and Portugal. It is identified by a black plastic nose and differences in lettering. See here for a fuller treatment of Leica Projection Lenses >.
Reflecta Agomar 90/2.4
This four-element design dates from a period when Reflecta took over Agfa’s production facility in Portugal in 1984 and is said to be identical to the Braun Ultralit 90/2.4. As with all these premier options, the package here is black metal jacket. Although its reputation is in the shadow of the Leica and Zeiss luminaries, it proves to be sharper in the field – or at least more uniform – but it’s clearly better at close range than far away: rendering useable (rather than perfect) corners in its comfort zone of around 1m.
Zeiss P-Sonnar and P-Planar
TBA
Conclusion
Losing finalists at Crufts are still considered fine examples of the breed. Likewise there’s a category of slide projector lenses we might judge ‘recommendable’ – with the caveats applicable to such optics (soft corners, low contrast, flare, CA, variable bokeh). In this group we find the Braun Ultralit/Agfa Agomar 90/2.4; all the Leica ColorPlans; the Zeiss Super Talon and (expensive) P-Sonnar (of which more was expected); Schneider’s Xenotar, Rollei’s S-Projar, and the unexpectedly tasty (and literally given away) Agfa Agomar 85mm [V2]. While other lenses may have interesting properties or styles of rendition, only this group can be considered ‘good enough’ on technical merit. They occupy ‘mid-Bronze’ territory, but frankly all other slide projector lenses are novelty items by comparison – at least with reference to pixel-level sharpness. Of course, pixel-level sharpness isn’t always needed, and there are great ‘looks’ achievable – particularly for videographers – in the Delta lens pool.
However, if we focus for a moment on technical characteristics alone – to date, three slide projector lenses have created an elite sub-category by achieving Silver-level performance. Sadly, the Schneider Vario-Xenotar 70-120 disqualifies itself as a finalist: it’s not as sharp overall as the top two (the rating difference is 2%); behaviour varies across the zoom range; geometric distortion (up to 4%) blights the short end (where it is sharpest); and chromatic aberration is present to a degree that will be intrusive in many scenarios.
Crowning one of the remaining contenders ‘King of the PJs’ is so difficult, and their performance within this category is so excellent, I would like to call this one a draw – then discuss favourites.
The Rollei AV-Apogon 90/2.4 is uniquely hi-res in Zone A – not merely sharp for a projector lens; sharp for a prime lens in 2022 – sharp enough to use on Micro FourThirds. Crisp. Wiry. Very sharp indeed. No other projector optic comes close: the next most impressive at this focal length is the Rollei S-Projar, but it has traditionally soggy corners, whereas the Rollei is just about useable. The AV-Apogon is distinguished by excellence at all working distances. Colour is rich and punchy and flare resistance is good for a lens of this type. Marks are deducted for less-than-perfect control of chromatic aberration, and above average mechanical (not optical) vignetting resulting in cat-eye deformation and bokeh swirl – this last property straying into subjective territory, but I would argue that this is a fault, not a feature.
Level-pegging the AV-Apogon is Leica’s ultimate evolution of the ColorPlan: the Super ColorPlan-P2 90/2.4: although conspicuously less sharp centre frame than the Rollei, the Leica is still better here than any other slide projector lens, and it’s noticeably superior in the corners, which makes it a more universally applicable lens. Chromatic aberration is better controlled (only the Agomar MC matches it) and mechanical vignetting is less noticeable, too.
If pressed to choose, the Leica is an obvious choice because of it’s all-round competence. Used carelessly, the AV-Apogon’s imperfections might spoil a shoot, but the Super ColorPlan P2 is solid, reliable and never fails to deliver that Leica look. Then again you probably have conventional taking lenses that do all that and more.
Of course, you need both: the Rollei AV-Apogon plays the bubble bokeh game in the most grown-up fashion. The Leica does Leica: creamier than creamy backgrounds rendered as impressionist paintings. It may be the only slide projector lens that allows a photographer freedom to place an in-focus subject anywhere in the frame, without falling into mush. Then again, the Rollei endows central-framed subjects with remarkable special sauce: the naturally softer outer zones combine with the biting clarity of the centre to boost subject separation by around half a stop, mimicking the look of an f2 aperture – with the added ‘mystery’ of subtle bokeh swirl stirred into the mix. The AV-Apogon doesn’t have Isco-smooth rendition, but its nisen is fine and delicately etched, and bokeh is more often ‘interesting’ than ‘distracting’.
Despite different characteristics, to my mind both have equal claim on the title ‘King of the PJs: the Leica, because it’s the least like a projector lens; the Rollei, because it’s the most like a projector lens. Is the finest Merlot the one that’s so good it could be Cabernet? Or is the best Merlot the one most typical – that fully expresses the potential of the varietal? Dirty Merlot. Your preference may swing with your feelings about projector lenses in general.
Epilogue
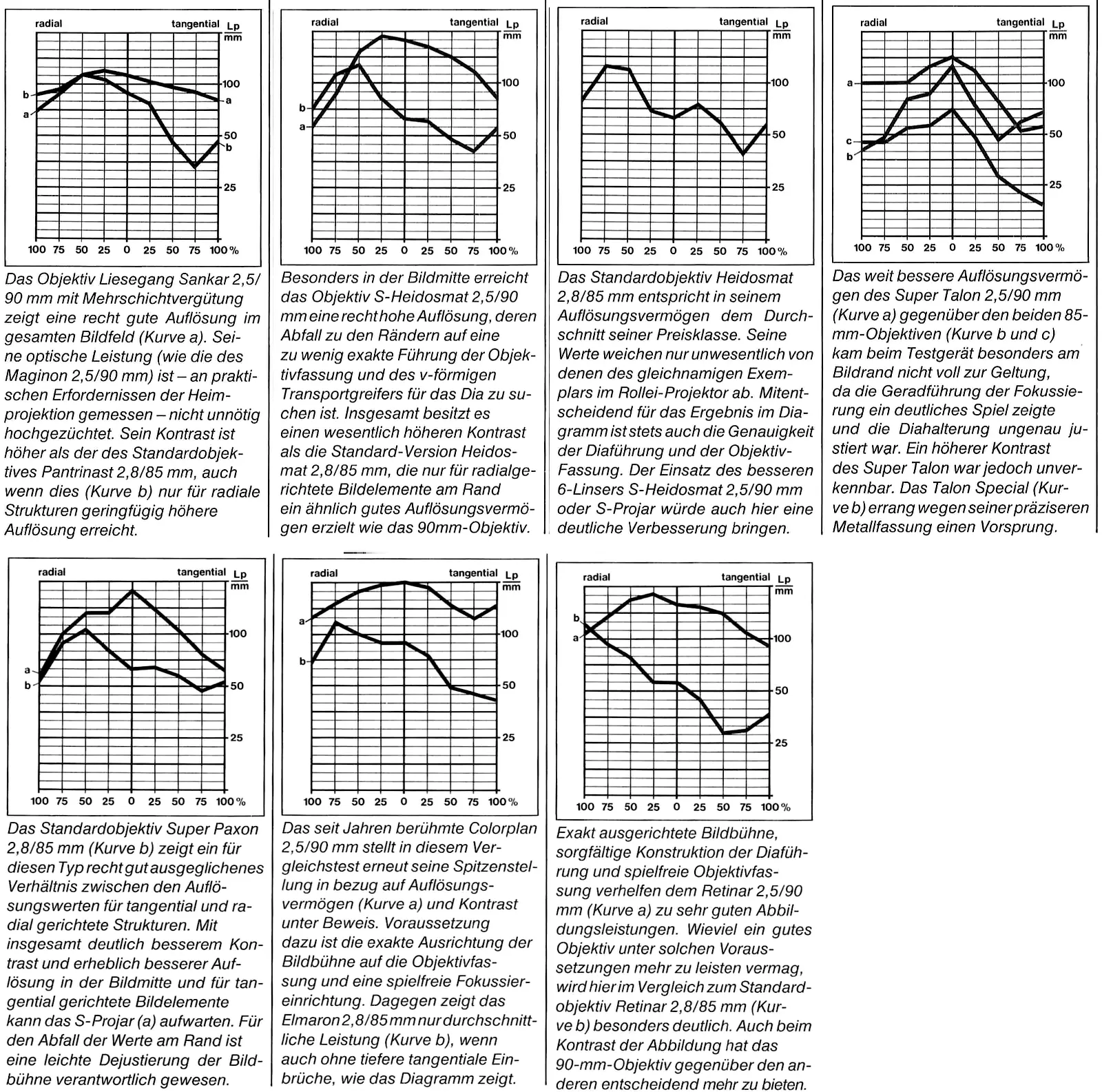
Sometime after concluding the main tranche of testing, an interesting group test of 14 projector lenses surfaced from Color Foto magazine’s December 1978 edition. Bear in mind as you compare the MTF charts they generated that most of the best lenses in the survey above were not yet born. However transparent their test methodology, they couldn’t see into the future.
Note the performance delta between the standard 85/2.8 triplets and the faster, more complex 90/2.5 variant – although in some cases the difference is localised to the frame centre. Note also the broad similarity between the Kodak Retinar 90/2.5 and S-Heidosmat 90/2.5. Using the (presumably single) sample S-Heidosmat tested, Color Foto recorded a radial corner performance lower than the standard Heidosmat, which seems anomalous – pointing to a centering issue with that particular unit. Perhaps a better sample would have given near-identical results.